Tintosmart is a project that looks to the future through an evolutionary space-time passage that recalls a famous film from the 1980s. Tintosmart is innovation with simple use technology, but development analytical complexity with the sole aim of allowing the user to proceed with coloring through quick and simple actions. The creative concept was founded, thanks to the pioneering peculiarities of the project, on the creation of an aerospace company style with the aim of coloring the universe.
To stay on the subject, the products and colors of the Tintosmart project have been named using references relating to programs, missions and human space explorations for what concerns the waterborne paints and the names of all the stars, constellations and asteroids for the colors of each color card.

Back to
the future
Back
to the color
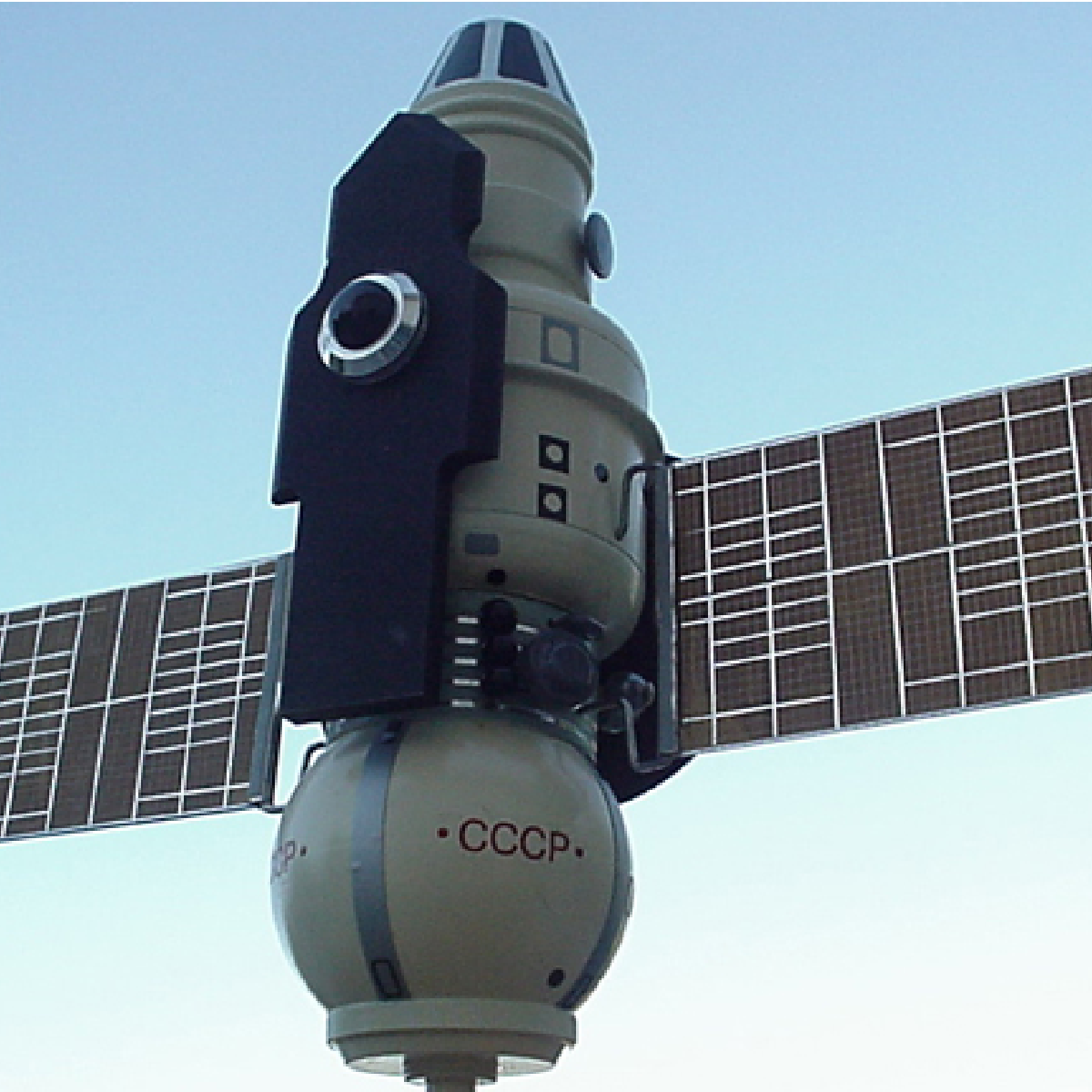
The Venera program
The Venera were a series of space probes developed in the Soviet Union to explore and collect data on the planet Venus.
As was often the case with Soviet explorations, the latest versions of the model were launched in pairs, with an interval of 1-2 weeks between launching the two probes.
They set a real record: they were the first man-made object to enter the atmosphere of another planet, land softly, resend images and perform a high-resolution radar scan of the surface, allowing in-depth studies on the geological conformation of the globe.
The series of probes, as a whole, can be considered a complete success for these reasons.
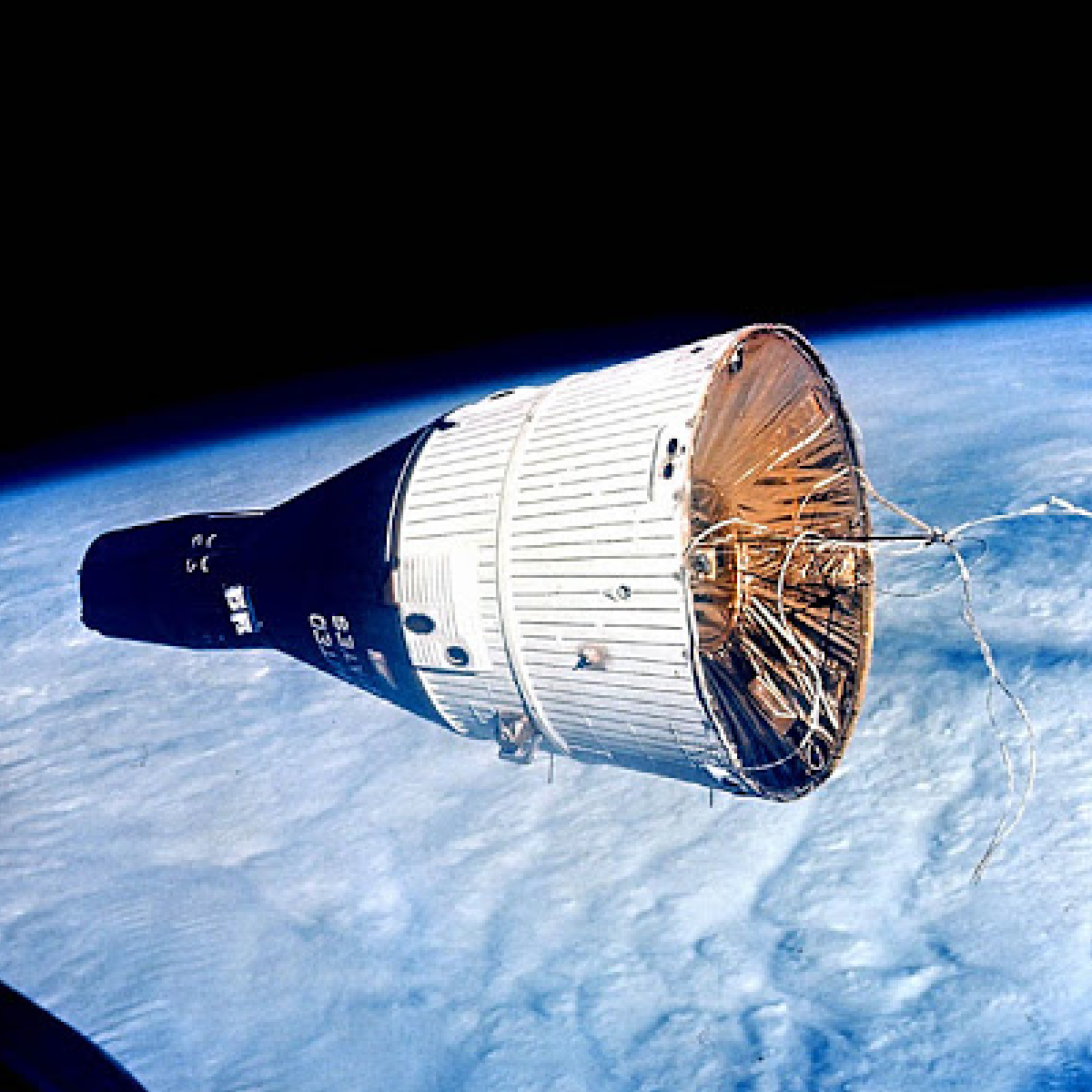

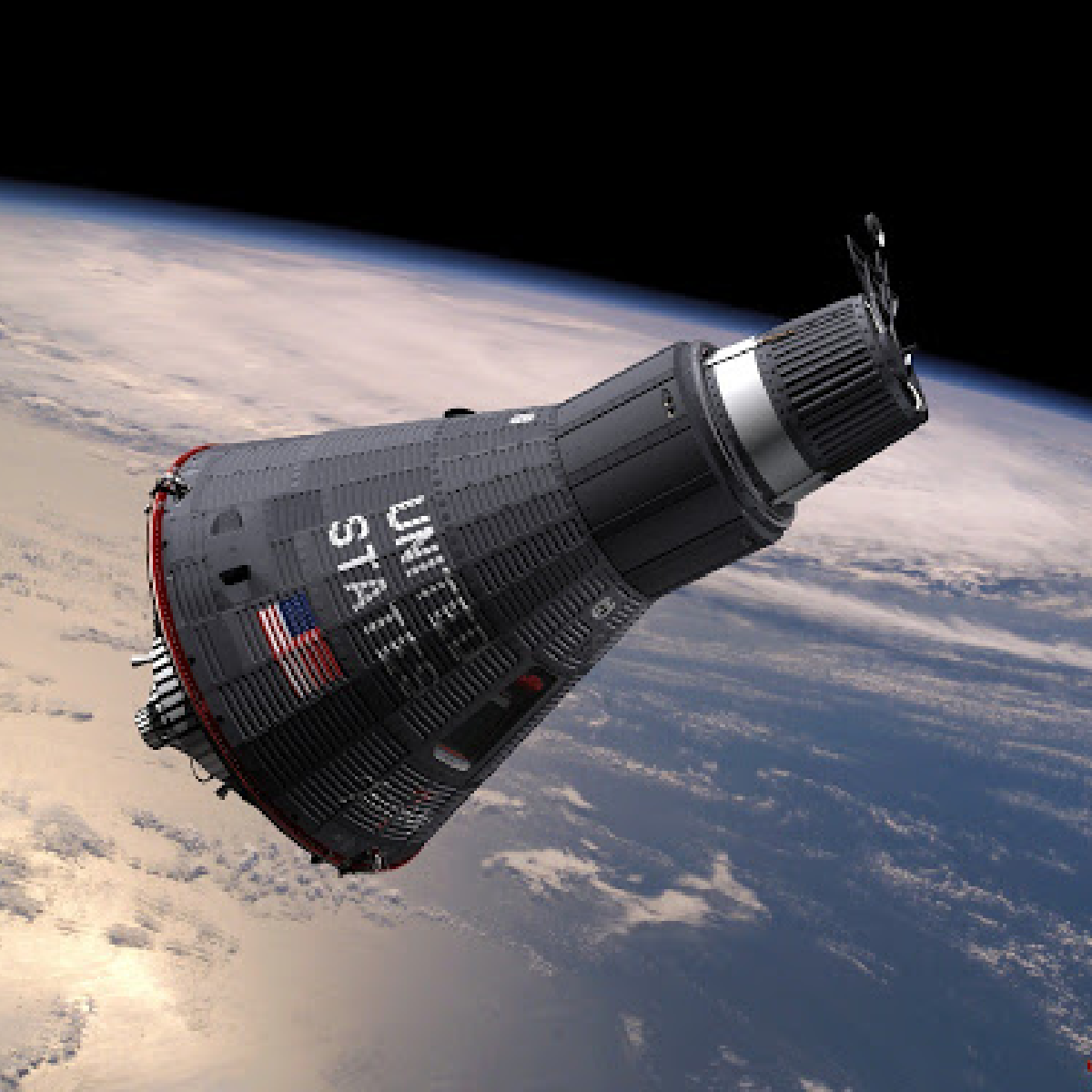
The Gemini program
Gemini is the second human space flight program undertaken by the United States.
The project was named Gemini as the spacecraft could accommodate a two-man crew. Conducted during the period 1963-1966, its purpose was to develop the techniques for advanced space travel then used during the Apollo program to bring man to the moon.
With the landing of Gemini 12 on November 15, 1966 and the respective closure of the special Gemini office, which took place on February 1, 1967, the program was declared definitively terminated.

The Mercury program
The Mercury program, or Project Mercury, was the first US program to include manned space missions. It was active between 1958 and 1963, during the presidency of Dwight Eisenhower first and the presidency of John Fitzgerald Kennedy then, with the aim of putting a man into orbit around the Earth. The initial design and research was carried out by the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), while the program was officially carried out by the newly formed NASA.
The name derives from Mercury, the Roman god protector of merchants and traders.

The Kepler program
The Mercury program, or Project Mercury, was the first US program to include manned space missions. It was active between 1958 and 1963, during the presidency of Dwight Eisenhower first and the presidency of John Fitzgerald Kennedy then, with the aim of putting a man into orbit around the Earth. The initial design and research was carried out by the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), while the program was officially carried out by the newly formed NASA.
The name derives from Mercury, the Roman god protector of merchants and traders.

The Lunar orbiter program
It consisted of a series of 5 unmanned probes launched by the USA in 1966 – 1967 with the task of taking photos of the entire lunar surface. All five missions succeeded and in total 99% of the Moon was mapped.

The ECHO-1 program
Launched by NASA in 1960, this passive satellite consisted of an inflatable sphere composed of a metallic Mylar film capable of reflecting radio waves. The purpose of the satellite was to verify the possibility of communicating between distant areas of the earth using, as a radio link, an object in orbit.

The VEGA program
Vega 1 and its twin Vega 2 were two Soviet space probes, part of the Vega Program. They were launched in 1984 with the aim of flying over Venus and Comet Halley.